Knee pain can significantly impact your daily life, hindering your ability to perform simple tasks and engage in activities you enjoy. However, with a thorough understanding of its causes and appropriate treatment options, you can regain control and improve your quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of knee pain, focusing on its association with sports injuries and arthritis. Let’s look into common Management of Knee Pain symptoms, what could be causing the pain, and offer effective strategies for relief and maintaining knee health, so you can get your life back!
Understanding Knee Pain and Its Causes
The knee joint is complex, consisting of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage that work together to provide stability and facilitate movement. Knee pain can stem from various sources, but two primary culprits are injuries and arthritis.
It is a common misconception that injuries only happen to athletes or as a result of overuse. In reality, injuries can occur to anyone at any time, regardless of how inconvenient it may be. Everyday activities such as exercising without a proper warm-up, assisting a friend with moving by lifting a heavy box, or simply squatting down to pick up your toddler can lead to knee pain and injuries. It is important to remember that knee injuries don't discriminate and can affect anyone, not just athletes.
Arthritis is a significant factor that contributes to knee pain and reduced mobility. This degenerative disease can impact individuals of all ages and backgrounds, making it essential to gain a deeper understanding of the condition. By understanding arthritis and its effects on the knee joint, you can explore various strategies to alleviate pain and regain control of your life.
Signs and Symptoms of Knee Injuries
Understanding the signs and symptoms of knee injuries resulting from sports activities is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Swelling, bruising, pain, instability, and difficulty bearing weight are common indicators of knee injuries. By differentiating between sprains, strains, ligament tears, and other common knee injuries, healthcare professionals can develop appropriate treatment plans to facilitate recovery.
Sports Injuries and Knee Pain
Sports injuries can have a significant impact on the knee joint, leading to pain and reduced mobility. Understanding the types of injuries commonly encountered in sports activities is crucial for grasping their effect on the knee.
Sprains, strains, ligament tears, and other injuries can occur as a result of various factors, such as sudden twists, impact, or repetitive stress on the knee. Let's take a closer look at these types of injuries and how they can affect the knee.
- Sprains: A sprain refers to the stretching or tearing of ligaments, which are the tough bands of tissue that connect bones together in a joint. In the case of knee sprains, they often occur when the knee joint is forced into an unnatural position or moves beyond its normal range of motion. This can happen during activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or landing improperly. The severity of a sprain can vary from mild (stretching of the ligament fibers) to severe (complete tear of the ligament).
- Strains: Strains, also known as muscle strains or pulled muscles, involve the stretching or tearing of muscles or tendons around the knee joint. They typically occur due to overstretching or overuse of the muscles and tendons. Activities that require repetitive or excessive stress on the knee, such as running, jumping, or lifting heavy objects, can lead to strains. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, muscle weakness, and limited range of motion.
- Ligament Tears: Ligament tears, particularly involving the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL), are common knee injuries, especially among athletes. These tears often result from sudden twisting motions or direct blows to the knee. ACL tears are frequently seen in sports like basketball, soccer, and skiing, where sudden stops, changes in direction, or awkward landings can place excessive stress on the ligament. MCL tears, on the other hand, are commonly associated with contact sports and involve an inward force applied to the knee.
Other Injuries: Besides sprains, strains, and ligament tears, there are various other knee injuries that can occur. These include meniscus tears, which involve damage to the C-shaped pieces of cartilage in the knee joint, as well as fractures, dislocations, and tendon injuries. These injuries can be caused by traumatic events, falls, accidents, or repetitive stress on the knee joint.
It is important to note that the severity and treatment of these injuries can vary depending on the specific circumstances and individual factors. Seeking medical attention and proper diagnosis are crucial to determine the extent of the injury and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, bracing, pain management, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
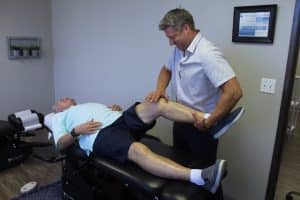
Dr. Michael Bell assesses and adjusts a patient's knee to relieve knee pain.
Arthritis and Knee Pain
Arthritis, a common condition affecting the joints, can also contribute to knee pain. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are two forms that commonly affect the knee joint. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect nearly everyone, especially in the 16-60 age range, and osteoarthritis is more common in women over the age of 50.
Osteoarthritis is a common degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the gradual degradation of joint cartilage, which is the smooth and flexible tissue that covers the ends of bones within a joint. The loss of cartilage leads to several debilitating symptoms, including pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
The gradual degradation of joint cartilage in osteoarthritis can occur due to a combination of factors, including age, genetics, obesity, joint overuse or injury, and metabolic conditions. Over time, the cartilage becomes worn down, frayed, and may eventually wear away completely, exposing the underlying bone.
As the cartilage deteriorates, the protective cushioning between the bones diminishes, causing the bones to rub against each other during joint movement. This friction can result in pain and discomfort. The pain experienced in osteoarthritis is typically described as aching or throbbing and can worsen with joint use or after periods of inactivity.
Inflammation is another hallmark feature of osteoarthritis. The body's natural response to the cartilage breakdown is to trigger an inflammatory reaction, leading to swelling and redness in the affected joint. This inflammation can further contribute to pain and stiffness.
Stiffness is a common symptom experienced in osteoarthritis, particularly after periods of rest or in the morning. The affected joint may feel stiff and difficult to move, making it challenging to perform daily activities.
While osteoarthritis commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, it can occur in any joint in the body. The severity of symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and the impact on an individual's quality of life can also vary.
Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve joint function. These may include pain management techniques, lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, assistive devices, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
Early diagnosis and proactive management of osteoarthritis can help individuals effectively control pain, reduce inflammation, and maintain joint mobility. Seeking medical attention and adopting appropriate treatment strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with osteoarthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, including the knees. It is characterized by persistent inflammation in the synovium, which is the lining of the joints. This inflammation is a result of the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, leading to joint damage and various symptoms. This immune response triggers the release of inflammatory substances, such as cytokines, which cause inflammation and damage to the joints. Over time, this chronic inflammation can lead to joint stiffness, pain, swelling, and ultimately, joint deformity and loss of function.
The inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis is not limited to the joints. It can also affect other organs and systems in the body, such as the skin, eyes, lungs, and blood vessels. This systemic involvement distinguishes rheumatoid arthritis from other forms of arthritis.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Women are more commonly affected by the disease than men, and it often begins between the ages of 30 and 50, although it can occur at any age.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in rheumatoid arthritis to prevent or minimize joint damage and disability. Rheumatoid arthritis treatment aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, slow down disease progression, and improve overall quality of life. Medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
In addition to medication, other treatment approaches for rheumatoid arthritis may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Physical therapy can help improve joint function, strengthen the muscles around the affected joints, and enhance mobility. Occupational therapy focuses on adapting daily activities to minimize joint stress and improve overall functionality.
Living with rheumatoid arthritis requires ongoing management and care. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals, self-care measures, and a holistic approach that includes exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate rest are essential for managing symptoms and maintaining joint health.
By understanding the nature of rheumatoid arthritis and its impact on the knees and other joints, individuals can work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and helps them live a fulfilling and active life despite the challenges posed by the disease.
Both forms of arthritis can result in significant discomfort, restricted movement, and joint deterioration.
Listen To Your Body When It Comes To Sports Injuries
Listen to your body to understand the signs and symptoms of knee injuries resulting from sports activities. By being in tune with your body, you can proactively care for your health through getting an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
If you are experiencing swelling, bruising, pain, instability, and difficulty bearing weight, these are common indicators of knee injuries, and it is recommended that you see a medical professional to get assessed.
By differentiating between sprains, strains, ligament tears, and other common knee injuries, healthcare professionals can develop appropriate treatment plans to facilitate recovery.
Recognizing Arthritis Symptoms in the Knee
Recognizing the specific symptoms of arthritis in the knee joint can help effectively manage the condition and seek appropriate treatment. Arthritis can cause a range of symptoms that significantly impact daily life and mobility. By being aware of these symptoms, you can take proactive steps to address them and improve your overall knee health. Some common symptoms of arthritis in the knee are as follows, and if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, schedule an appointment with a professional healthcare provider:
- Joint Stiffness: One of the hallmark symptoms of knee arthritis is stiffness in the joint. Individuals may experience difficulty in starting movement after periods of rest or prolonged inactivity. The stiffness can make it challenging to bend or straighten the knee fully, resulting in a limited range of motion.
- Pain during Movement: Arthritis in the knee often leads to pain when the joint is in motion. Activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for prolonged periods can trigger discomfort and pain. The pain may range from mild to severe, and it may be described as aching, throbbing, or sharp.
- Swelling: Inflammation is a common feature of arthritis, and it can cause swelling in the knee joint. The swelling may be localized or more widespread, leading to visible enlargement of the knee. Swelling can contribute to joint stiffness and further limit mobility.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Arthritis can gradually restrict the range of motion in the knee joint. As the condition progresses, individuals may find it increasingly challenging to fully flex or extend the knee. This limitation can affect activities that require a wide range of knee motion, such as squatting, kneeling, or participating in sports.
When individuals recognize these symptoms of arthritis in the knee, it's essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Based on the diagnosis, various treatment options can be explored to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and slow down joint degradation. These may include a combination of medication (such as pain relievers, corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs), physical therapy, assistive devices (like braces or orthotics), lifestyle modifications (such as weight management and exercise), and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
By recognizing the specific symptoms of arthritis in the knee joint, individuals can take proactive steps to manage the condition effectively. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall knee health, allowing individuals to lead a more active and fulfilling life.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain Relief
When it comes to knee pain, various treatment options can provide relief and promote healing. Depending on the cause of knee pain, different approaches may be recommended. At Vitality Integrative Wellness, our medical professionals can work with you to give you a diagnosis and create the best treatment plan for you.
Non-Surgical Approaches for Sports Injuries
Knee injuries and pain don’t have to end in surgical repair. For knee pain resulting from sports injuries, non-surgical approaches can be highly effective in managing pain and facilitating recovery.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation programs play a crucial role in the treatment and recovery of knee injuries. These programs are specifically designed to meet the individual needs of patients and aim to strengthen the knee, restore function, and alleviate pain. Here's an elaboration on how physical therapy and rehabilitation can benefit individuals with knee injuries:
- Strengthening the Knee: Physical therapists employ a variety of exercises and techniques to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint. Strengthening exercises target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and other surrounding muscles, helping to provide better support and stability to the knee. This increased muscle strength can help prevent further injury and improve overall knee function.
- Restoring Function: Knee injuries can lead to limitations in range of motion and difficulty performing everyday activities. Physical therapists work with patients to improve joint mobility and restore functional movement. They employ stretching exercises, joint mobilization techniques, and manual therapy to increase flexibility and restore normal knee function. Through targeted exercises and functional training, patients can regain the ability to walk, run, and engage in other activities without pain or limitations.
- Alleviating Pain: Pain management is a key aspect of physical therapy and rehabilitation. Therapists use various techniques such as ice or heat therapy, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and manual therapy to reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint. They also educate patients on proper body mechanics and movement patterns to minimize stress on the knee and alleviate pain during activities.
- Improving Balance and Stability: Knee injuries can affect balance and stability, increasing the risk of falls or further injury. Physical therapy programs often include exercises that target balance and proprioception (awareness of body position), helping patients regain their stability and reduce the risk of re-injury. Balance training exercises may involve standing on one leg, using stability boards or balance discs, and performing specific movements to challenge the body's equilibrium.
- Individualized Approach: Each person's knee injury is unique, and physical therapy and rehabilitation programs take this into account. A skilled physical therapist will conduct a thorough evaluation of the individual's condition and design a personalized treatment plan based on their specific needs, goals, and limitations. The program may be adjusted over time as the patient progresses and responds to treatment.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation are often recommended as a conservative approach before considering surgical intervention for knee injuries. These programs not only help in the recovery phase but also serve as a preventive measure to minimize the risk of future knee problems. By working closely with a physical therapist, patients can receive expert guidance, support, and motivation throughout their rehabilitation journey, ultimately achieving improved knee function, pain relief, and an enhanced quality of life.
Managing Arthritis-Related Knee Pain

Red light therapy is an effective tool in alleviating pain.
For individuals experiencing knee pain due to arthritis, various strategies are available to manage symptoms and promote overall knee health. These approaches can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve the individual's quality of life. Here's an elaboration on some effective strategies:
- Medications: Medications are commonly used to manage arthritis-related knee pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to provide targeted pain relief and decrease inflammation. Additionally, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biological agents may be recommended to slow down the progression of arthritis and preserve knee function.
- Regenerative Medicine: Regenerative medicine techniques, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or stem cell therapy, have shown promising results in managing knee pain caused by arthritis. PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient's own platelets into the affected knee, which can stimulate tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation. Stem cell therapy utilizes stem cells derived from the patient's body or donor sources to promote tissue repair and decrease inflammation in the knee joint.
- Red Laser Therapy: Red laser therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), is a non-invasive treatment option that uses low-intensity laser light to reduce pain and inflammation in the knee. The laser light penetrates the skin and stimulates cellular activity, promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and providing pain relief.
- Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises: Regular stretching and range of motion exercises can help maintain flexibility and mobility in the knee joint. These exercises can improve joint function, reduce stiffness, and alleviate knee pain caused by arthritis. Physical therapists can provide guidance on specific stretching and range of motion exercises tailored to an individual's needs.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with knee pain caused by arthritis. Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joint, leading to increased pain and discomfort. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can manage their weight effectively, reducing the strain on the knee and improving overall knee health.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of these strategies may vary depending on the severity and type of arthritis. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a rheumatologist or orthopedic specialist, who can provide personalized recommendations and guidance based on an individual's specific condition.
Incorporating a combination of these strategies, along with a comprehensive arthritis management plan, can significantly improve knee pain symptoms and enhance overall knee health for individuals living with arthritis.
Ditch the Pain and Take Your Life Back
Don't let knee pain and arthritis hold you back in life. It's time to take action and pave the way for a healthier, pain-free future. At Vitality Integrative Wellness, we are dedicated to helping you on this journey and witnessing your thriving success.


